Turkishdoc
Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome Diagnosis, Treatment Methods, and Risks
Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome, often known as WPW, is an extremely uncommon illness that is characterized by aberrant electrical conduction in the heart. This syndrome is characterized as an abnormality of the heart that is present at birth and involves an additional channel in the conduction of the electrical impulses in the heart. It is a congenital (existing at birth) condition. This extra pathway has the potential to lead to rapid and irregular conduction of electrical signals between the ventricles and the atria, which in turn can cause tachycardia (an excessively fast heartbeat) and other potentially life-threatening consequences.
Methods of Diagnosis
The following is a list of the primary diagnostic approaches that are utilized for Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
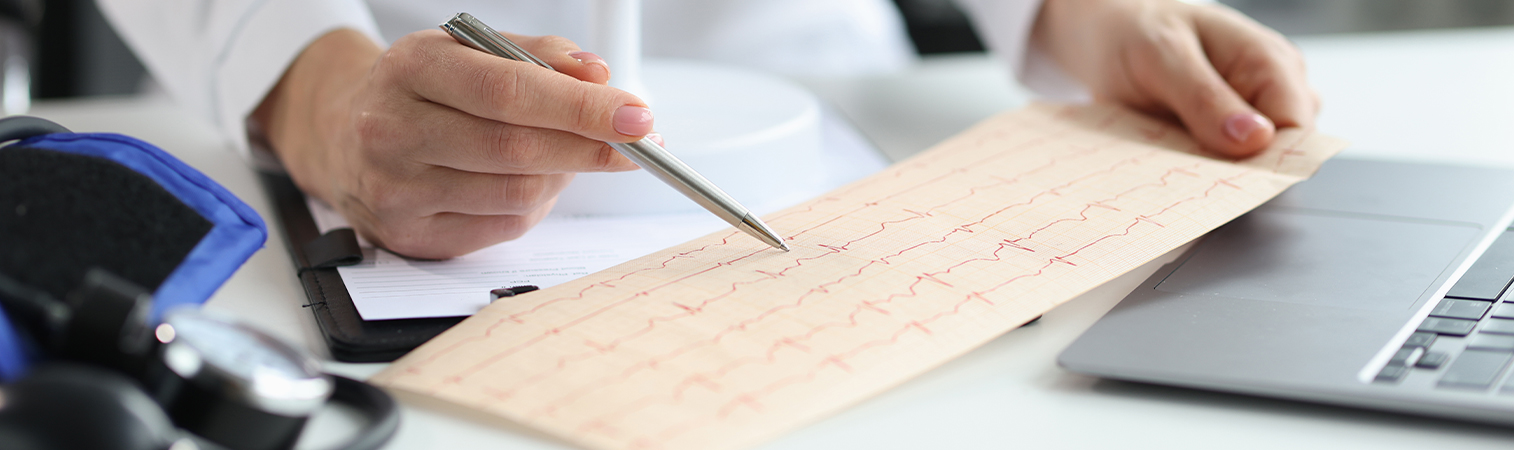
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a diagnostic method for monitoring and recording cardiac electrical activity. Patients with WPW syndrome are typically seen to have pre-existing ventricular excitation (shortened PR interval) and a prominent wave known as a “delta wave”.
- Holter Monitor
This device monitors the electrical activity of the heart continuously for a period of 24 to 48 hours. This makes it easier to pinpoint the exact moments when symptoms and aberrant cardiac rhythms manifest themselves.
- Research Involving Electrophysiology (EPS)
To perform this test, catheters are first inserted into the heart, and then the heart’s response to the electrical impulses produced by the catheters is evaluated. The specific location of extra pathways can be determined with the use of EPS, as can the features of these pathways.
Treatment Methods
The treatment techniques for Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) can differ from patient to patient based on the severity of the patient’s symptoms as well as the potential risk of complications. Here are some therapeutic approaches utilized for WPW syndrome:
Medication: Medication is necessary for the treatment of WPW syndrome in some patients to slow the heart rate and control irregular rhythms. Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic medicines are some examples of the types of medications that can be used for this purpose.
Ablation Using A Catheter: To eradicate aberrant electrical pathways, this surgery makes use of specialized catheters that are placed into the heart. Ablation with a catheter is typically a successful and long-lasting therapy option. people who do not respond to medication or people who want a more final solution are good candidates for this treatment.
Electrical Cardioversion: Patients who are suffering from potentially life-threatening rhythm irregularities as a result of WPW syndromes, such as severe tachycardia or atrial fibrillation, have the option of undergoing electrical cardioversion. Shock waves are utilized in this treatment approach to restore a normal rhythm to the patient’s heart.
Ablation Performed Surgically: When catheter ablation fails to achieve the desired results or when there are other exceptional conditions surrounding the patient, surgical ablation may be the better option. During this procedure, the rib cage is cut open, and the aberrant electrical pathways are either severed or stopped using surgical techniques.
Lifestyle Changes: Patients whose symptoms are minor or who do not require the aforementioned treatment approaches may be able to control their symptoms by adjustments in their lifestyle. Alterations to one’s lifestyle, such as the management of stress, appropriate exercise, and sleep habits, as well as the reduction of one’s usage of tobacco products and alcohol, can help lessen the consequences of WPW syndrome by promoting overall heart health.
In conclusion, there are a variety of therapy modalities available for patients who have WPW syndrome, and the choice of treatment is dependent on the intensity of the patient’s symptoms as well as their quality of life. The conditions of their patients will be evaluated, and the physicians will devise the most effective course of therapy.
What Are the Risks of Wolf Parkinson White (WPW) Syndrome Treatment?
Treatment for Wolf Parkinson White (WPW) Syndrome carries certain risks, just like any medical procedure. Here are some of the risks you should be aware of for WPW syndrome treatment:
- Medication
Medicines are typically the therapy option with the lowest risk, although they can have unintended consequences. The manifestation of adverse effects varies greatly from individual to individual, and some people may have symptoms such as lightheadedness, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Additionally, the efficacy of the drugs may lessen over time, which may necessitate modifications to the prescribed dosage.
- Ablation Using A Catheter
Catheter ablation is a surgery that often results in a successful and permanent therapy; nevertheless, problems can arise while the procedure is being performed. A variety of complications might arise, including injury to the blood arteries of the heart, hemorrhage, infection, and thrombosis. (clot formation). During the process of ablation, there is also the possibility of damaging healthy tissue by accident.
- Electrical Cardioversion
Shock waves are used in the process of electrical cardioversion, which is done to restore the heart to its normal rhythm. Side effects include skin burns, low blood pressure, and brief abnormalities in heart rhythm have been known to occur. Additionally, if the cardioversion is unsuccessful, it may be necessary to try another technique.
- Ablation Performed Surgically
Because the rib cage has to be opened to access the heart during surgical ablation, the procedure is associated with a higher risk than other treatment approaches. Bleeding, infection, difficulties from the anesthetic, and thrombosis are some of the most common hazards associated with surgical operations. (clot formation). In addition, there is always the possibility that the surgical ablation may not be successful, and there is also the possibility that the surgery can cause damage to good tissue.
Treatment options and potential side effects need to be evaluated on an individual basis for each patient. The state of the patient’s health, as well as their age, the intensity of their symptoms, and the potential dangers of complications, all play a role in how the doctor decides which treatment technique is best. Patients must communicate openly and honestly with their healthcare providers to formulate an appropriate treatment strategy that takes into account both the potential drawbacks and advantages of the proposed interventions.