Turkishdoc
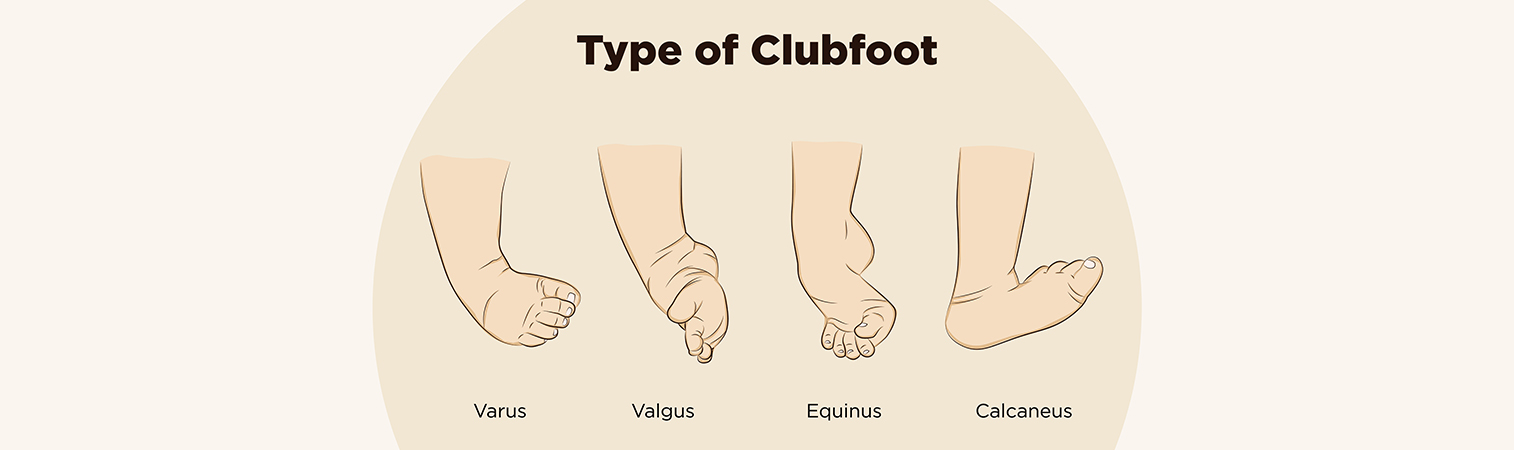
What Is A Clubfoot?
Clubfoot is a congenital anomaly in which one or both feet are crooked. Therefore, this condition in babies can be diagnosed immediately. This common congenital defect must be treated. Otherwise, one of the possible issues will be an inability to walk or walking disorders. There is no clear cause for this idiopathic foot deformity. Mild or severe cases can be seen in this condition. Since it is usually seen in both feet, it is important to treat it immediately as a baby. In some cases, surgical methods can also be applied in clubfoot syndrome, where non-surgical treatments are also successful. Since it is not possible to heal on its own, it is a condition that requires immediate treatment by a doctor with appropriate procedures.
Symptoms Of Clubfoot
It is possible to observe the symptoms of clubfoot both before and after birth. At 18 and 21 weeks, this foot deformity can be seen with ultrasonography controls in the womb. After birth, clubfoot, which is also visible, can be easily diagnosed. In this condition, in which the calf muscles are underdeveloped, the baby does not feel any pain. Therefore, the most important symptom seen in a baby is the crooked appearance of one or both feet. The main symptoms appear when the baby starts to grow. Other symptoms of clubfoot include:
- Bending the top of the foot downward and inward
- The affected leg is shorter
- The calf muscles of clubfoot are less developed and less mobile
- Walking by stepping on the outside of the feet
- Difficulty walking
Clubfoot is also disturbing and worrying in terms of appearance. Without early treatment, calluses, joint deformities, deformities, and arthritis can develop. In some cases, this foot deformity is also associated with hip dislocation and spina bifida. In short, even the presence of at least one of these symptoms can be decisive for this condition. It is important that clubfoot, which is a serious congenital anomaly, is treated by a pediatric orthopedist in the first weeks. Late treatment may lead to surgical intervention.
Causes Of Clubfoot
First of all, clubfoot is an idiopathic congenital anomaly. Therefore, it is not possible to say that there is a definite cause. According to the results of studies, genetic or environmental factors are important factors in this condition. There are also some risk factors for clubfoot. Among the risk factors for clubfoot are the following:
- Smoking by the mother during pregnancy can trigger the development of this condition.
- The presence of clubfoot in parents or siblings can put the newborn baby at risk.
- Gender is also an important factor in this case. because this foot deformity is more common in male babies than in female babies.
- Detection of chromosomal disorders
- Shorter tendons connecting the foot muscles to the bone
- Not enough amniotic fluid during pregnancy
- Developmental disorders in foot bones and joints
In general, these are the risk factors for clubfoot. This condition, which is recognized in infancy, should be treated as soon as possible. The treatments for this foot deformity, which concerns both the baby and the parents, are applied with different methods according to its severity.
Treatment For Clubfoot
It is important to start treating clubfoot in the first few weeks after birth. It is a condition that the doctor can recognize immediately, as it needs to be diagnosed before treatment. Foot shape and posture facilitate its diagnosis. It is not possible to intervene before birth for clubfoot, which is also diagnosed before birth. However, parents should be informed and ready for this. When this foot deformity is diagnosed after birth, appropriate treatment methods are started. The main purpose of the treatment methods to be applied is to correct the foot and leg appearance before the baby reaches the walking stage. Thus, it is to prevent problems that may occur in walking. Below is important information about treatment methods for clubfoot:
Stretching and casting (Ponseti method): The Ponseti method, which is one of the non-surgical methods, is the most commonly used treatment method in these cases. This method aims to correct the baby’s foot posture with a cast. After the baby’s feet have been properly positioned, they are placed in a plaster cast for a week. These casts are changed every week. During the 2 months, the casts are changed, and an improvement is expected. Before the last cast is applied, a procedure is required to lengthen the achilles, the strongest tendon. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and the tendon is lengthened through a small incision. After this procedure, the foot is placed in a cast again, the achilles is allowed to heal, and the foot is allowed to recover for 2-3 weeks. Therefore, it can be said that the plastering method was one of the first methods used. During this process, the doctor always checks the color, temperature, blood circulation, and movement of the fingers.
Bracing for Clubfoot: Besides plaster treatment, supportive treatment is also applied. Bracing is one of the most effective auxiliary treatment methods for this. It is necessary because the clubfoot cannot be completely corrected without this treatment method. After the baby has been fitted with a supramalleolar orthosis with a bar, it is used for the period specified by the doctor until the baby reaches kindergarten age. Bracing for clubfoot is therefore an adjunctive treatment.
Surgery: If clubfoot does not improve with the above treatment methods, surgical intervention is necessary. This method aims to bring the joints and bones of the foot into a suitable shape. Between 6 months and 1 year of age, supportive equipment is used after this surgery. After the surgery, special boots are designed for the baby to wear for a certain period until the baby is 4-5 years old. These boots, which are designed within certain measures, are fastened with metal rods. After wearing the boots that provide the appropriate posture on the feet, exercises are performed regularly. These exercises are given by a physiotherapist, and parents should have their children suffering from clubfoot do them. Arthritis, joint stiffness, and limitations of movement can be seen in this treatment method, which causes some complications. After wearing this auxiliary equipment, the child should be checked by a doctor for a certain period.
These treatment processes usually take a long time. If the warnings during the treatment process are not heeded, it may relapse again. Therefore, the person can continue to move with appropriate devices and equipment. Since it is a sensitive and important treatment process, parents should be very careful about this. A full recovery is possible if the rules and warnings in the treatments are followed and regular check-ups are scheduled.
In conclusion, clubfoot syndrome is a condition in which one or both feet of newborn babies are turned inward. It is easy to diagnose because it is physically recognized directly. There are some risk factors for this condition, which have no clear cause. Treatment methods include special plaster casts, wires, and orthopedic supports. It is also important to start treatment within 1-2 weeks after birth. Since it is a serious and sensitive foot deformity, treatment takes a long time. When the rules of treatment are strictly followed and regular doctor visits are made, clubfoot will improve. Otherwise, some problems are likely to reappear when the child grows up. Therefore, since it is a serious treatment, parents should be sensitive and careful until the end of the process.