Turkishdoc
What Is A Brachial Plexus Injury?
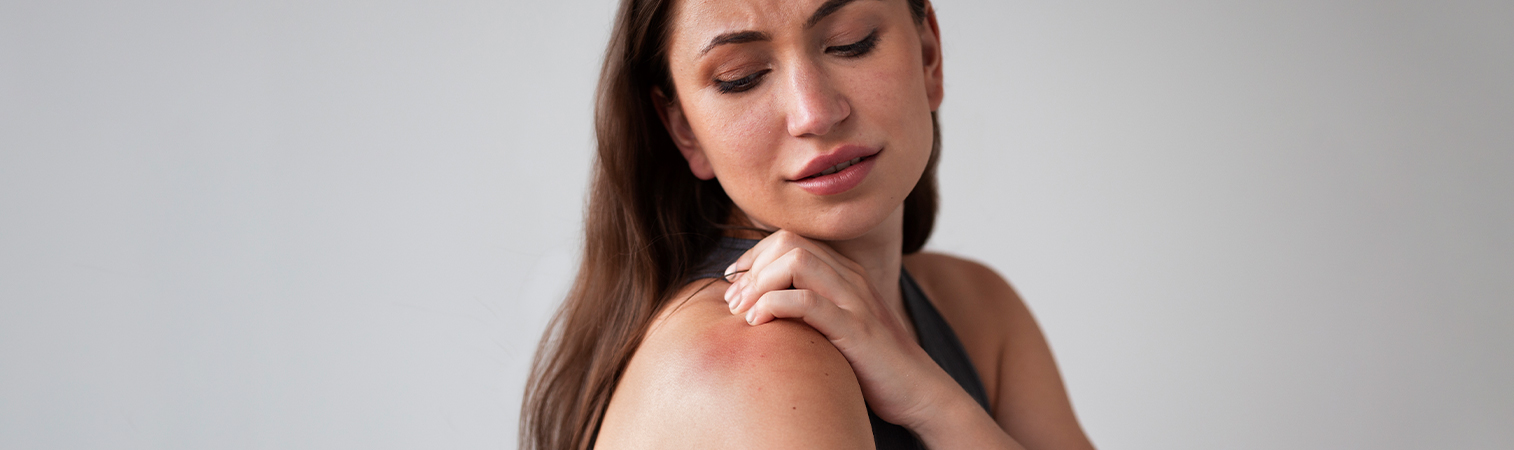
A brachial plexus injury is an injury caused by stretching and compression of the nerve net extending from the spinal cord to the hand. The brachial plexus is defined as the network of nerves from the vertebrae in the neck to the arm. The scapula, arm, and shoulder muscles are the areas most affected by this injury. As a result of this damage, there is weakness in the muscles of the hand and arm. There may even be numbness (loss of sensation) in the arm. This condition, which affects the movement of the arm, can occur during infancy or due to environmental factors. Some treatment methods can be used to treat minor or severe brachial plexus injuries.
Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms
Brachial plexus injury symptoms are common. These symptoms in one arm can last for minutes in some cases and for days in others. Symptoms may also vary depending on the severity of the injury. The following are common brachial plexus injury symptoms:
- Numbness and weakness after the injury
- Electric shock sensation
- Similar symptoms in both arms
- Neck pain
- Weakness in hand, shoulder, and arm muscles
- Loss of functionality of the hand, shoulder, and arm limbs
The above symptoms can be observed as a result of minor or severe damage. Minor brachial plexus injury symptoms are called stingers or burners. Serious symptoms occur when the brachial plexus injury is torn, ruptured, or injured. A brachial plexus injury that causes disability and difficulty is damage that needs to be treated. Therefore, if you have weakness in both arms, loss of sensation, and neck pain, which are the most important symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Causes Of Brachial Plexus Injury
A brachial plexus injury caused by a strong tilt of the head sideways or downwards can cause pain or a burning sensation. The nerves are stretched and injured when the neck is suddenly twisted sharply. Pushing the arm down and the head forward also causes this deformity. Other causes of brachial plexus injuries are as follows:
- Collisions during the playing of contact sports such as soccer, volleyball, or basketball
- Compression of the baby during labor
- Forced pulling or stretching of the arm
- Vehicle accident
- Physical violence
- Falling
- Radiation therapy
In general, these are the causes of brachial plexus injury. These causes produce this injury at certain severities. Neuropraxia, rupture, and avulsion are the levels of this condition. The mildest level is neuropraxia, and this refers to the ability to heal on its own. A partial or complete rupture of the nerves is called a rupture. Surgical recovery is possible. The most serious brachial plexus injury is defined by the severity of the avulsion. When it occurs as a result of the nerve roots rupturing from the vertebral marrow, it can be very difficult to treat, even with surgery. In addition to the causes of this deformity, there are also some risk factors. Risk factors include contact sports and driving at high speeds. Therefore, it is necessary to be more careful to prevent these risks. In this condition, which is seen in infants and adults, some treatment methods are applied according to its severity.
Treatment For Brachial Plexus Injury
A brachial plexus injury is a condition that must be treated as it presents with some important symptoms and affects the person’s health. The diagnosis of this injury will require a physical examination and other diagnostic methods. Other diagnostic methods are X-rays, electromyography, magnetic resonance imaging, and computed tomography. These methods are applied according to the symptoms and severity of the brachial plexus injury. There is, therefore, a detailed diagnosis.
Once a brachial plexus injury has been diagnosed, appropriate treatment can begin. Different treatment methods are applied depending on the type, duration, and severity of the injury. If there are stretched nerves, they can be treated without surgery. Usually, physical therapy or surgery is used for this condition. In most cases, conservative treatment methods are used for brachial plexus injuries and are effective. Below is important information about the treatment methods for brachial plexus injuries:
Physical therapy: Physical therapy is the primary treatment for mild brachial plexus injuries. This treatment method, which enables muscles and bones to fulfill their functionality, also eliminates nerve deformation. Individualized physical exercises are prepared for the affected area and performed together. Physical therapy is a treatment method that can be applied at the beginning of this condition as well as after surgery. It is possible to restore the functionality of the shoulder, hand, arm, elbow, wrist, and finger bones and joints with the exercises in this treatment.
Orthopedic supports: Orthopedic supports are an auxiliary treatment. Splints are used to prevent the hand from curling inward, preventing the joints from being arrested. Shoulder straps and wrist braces can also be used to support the joints. Compression gloves keep hand edema and brachial plexus injury from interfering with daily life. Heating, TENS, and exercise therapies are also used to prevent the pain caused by this condition.
Surgery: The most severe brachial plexus injuries can be treated with surgery. Surgery is the first line of treatment, especially when these nerves are torn or severed. Symptoms such as pain, loss of sensation in the affected limb, and immobility may not improve with physical therapy alone. It should be noted that surgery is not effective for very serious damage.
In surgical treatment, different procedures are applied depending on the severity of the damage. These procedures are divided into four categories: neurolysis, nerve transfer, nerve graft, and muscle transfer. The neurolysis procedure is used to remove the nerve from the scar tissue. With the nerve transfer procedure, if the nerve root is severed from the vertebral marrow, a different nerve is taken and connected to the non-functioning one. A nerve graft procedure removes the damaged part of the brachial plexus and replaces it with a new nerve. A muscle transfer procedure transfers a working muscle tendon to a non-functioning tendon to restore muscle function in the hand.
In conclusion, brachial plexus injury is a condition in which the functions of the arm and hand, such as sensory perception and control of movement, are damaged as a result of some traumas. As a consequence of this injury, shoulder, hand, and arm functions may decline, and even paralysis may occur. These disorders caused by strain on the arm, shoulder, or neck can also expose the baby during infancy. Depending on the severity, physical therapy or surgery is used to restore the function of the hand, arm, shoulder, and neck. However, in the case of an extremely severe brachial plexus injury, even surgery is not a salvage treatment. Therefore, the most common symptoms of muscle weakness, pain, or loss of sensation in some parts of the body should be referred to a doctor. Diagnostic methods will help determine the appropriate treatment and minimize this deformity.