Turkishdoc
What Are Cardiac Tumors? Types, Symptoms, and Causes
Tumors that spread to the heart from other organs are called cardiac tumors. In particular, tumors originating from the lungs are the cause of their formation. They are seen in different types by settling in and growing in many parts of the heart. The size of cancerous or non-cancerous cardiac tumors also varies depending on the location of the heart. Lymphoma and leukemia cancers also have a high rate of spreading to the heart. Although some of these tumors are benign, they can turn into malignant tumors as they grow. Because they spread metastatically, cancer cells from many parts of the body can spread to the heart. These tumors first settle in the heart membrane and then spread to the heart muscle. Especially if it is malignant, it can put a person’s life at risk.
Cardiac Tumor Types
Many types of cardiac tumors can occur. Tumors that do not originate in other organs and develop in the heart are called primary heart tumors. Primary heart tumors are usually benign and heal easily. Tumors caused by cancer cells that spread from another organ or tissue are called metastatic heart tumors. Metastatic heart tumors that spread from different parts of the body are always malignant. These heart tumors are also classified into different types. Metastatic heart tumors can also be called secondary cardiac tumors. It is possible to examine these types of cardiac tumors in two different groups.
- Benign Primary Cardiac Tumors
Almost all primary cardiac tumors are benign. Only a few can be malignant. Although most are benign, if left untreated, they can grow and endanger a person’s life. Benign primary cardiac tumors include myxoma, lipoma, papillary fibroelastoma, and hemangioma. These cardiac tumors occur in adults. Cardiac rhabdomyoma, hamartoma, teratoma, and fibroma are the primary cardiac tumors seen in children. Below is information about the types of benign primary cardiac tumors in adults and children:
- Myxoma
The most common benign primary cardiac tumor. More common in women, these cardiac tumors occur in the left atrium on the left side of the heart. The exact cause of myxoma is unknown, but in some cases, it can be removed surgically.
- Lipomas
Originating in the endocardium or epicardium, these tumors can affect people of different ages. Occurring asymptomatically, a lipoma can be small or large. This tumor, which develops in the left ventricle, atrial septum, or right atrium of the heart, can cause arrhythmias in some cases.
- Papillary Fibroelastomas
These primary tumors often occur on the heart valves, particularly the aortic and mitral valves. They can occur in people of any age but are more likely to occur in people over 60. As they develop, this type of tumor can cause embolism and may need to be removed surgically.
- Hemangioma
This is a benign primary cardiac tumor that is usually asymptomatic. Hemangioma can occur in people of all ages and can be detected during tests for different reasons.
- Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
It is one of the most common benign cardiac tumors in infants and children. These benign primary cardiac tumors go away on their own without treatment.
- Hamartoma
Also called histiocytoid cardiomyopathy or Purkinje cell hamartoma, this heart tumor also occurs in children. It can affect the child’s heartbeat.
- Teratoma
This heart tumor develops in the pericardium and can also develop in the large blood vessels connected to the heart.
- Fibroma
This heart tumor grows in the ventricular muscles of the heart and may require surgery if it progresses. Otherwise, it can cause the child to develop some serious heart problems.
Malignant Primary Heart Tumors
Although malignant primary heart tumors are rare, there are several types. Sarcoma is the most common malignant heart tumor and has two subtypes: rhabdomyosarcoma and angiosarcoma. Angiosarcoma is a type of sarcoma that occurs in adults, while rhabdomyosarcoma occurs in infants and children. In addition to sarcoma, malignant primary cardiac types include lymphoma and malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Malignant fibrous histiocytomas develop in the left atrium of the heart and adversely affect blood flow. Lymphoma in the lymph nodes or bone marrow is particularly common in people with AIDS.
In addition to benign and malignant primary heart tumors, there are other types of tumors. These tumors can be benign or malignant. Mesothelioma and paraganglioma are among these heart tumors. Paraganglioma develops at the base of the heart, while mesothelioma develops in the pericardium.
Secondary Cardiac Tumors
There are also malignant cardiac tumors that spread to the heart from other organs and tissues, causing tumors to form. These are also called secondary or metastatic cardiac tumors. Cancers that occur in different parts of the body and have a high risk of spreading to the heart include:
- Stomach cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Cancer of skin tissues
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Liver cancer
- Lymphoma
- Large bowel cancer
Causes of Cardiac Tumors
To determine what causes cardiac tumors, it is first necessary to consider two different tumors. While the causes of primary heart tumors are not known for certain, the causes of metastatic heart tumors are known. Metastatic heart tumors, also called secondary tumors, are when cancer cells from another part of the body spread to the heart. With this jump, it starts to develop and settle in the heart.
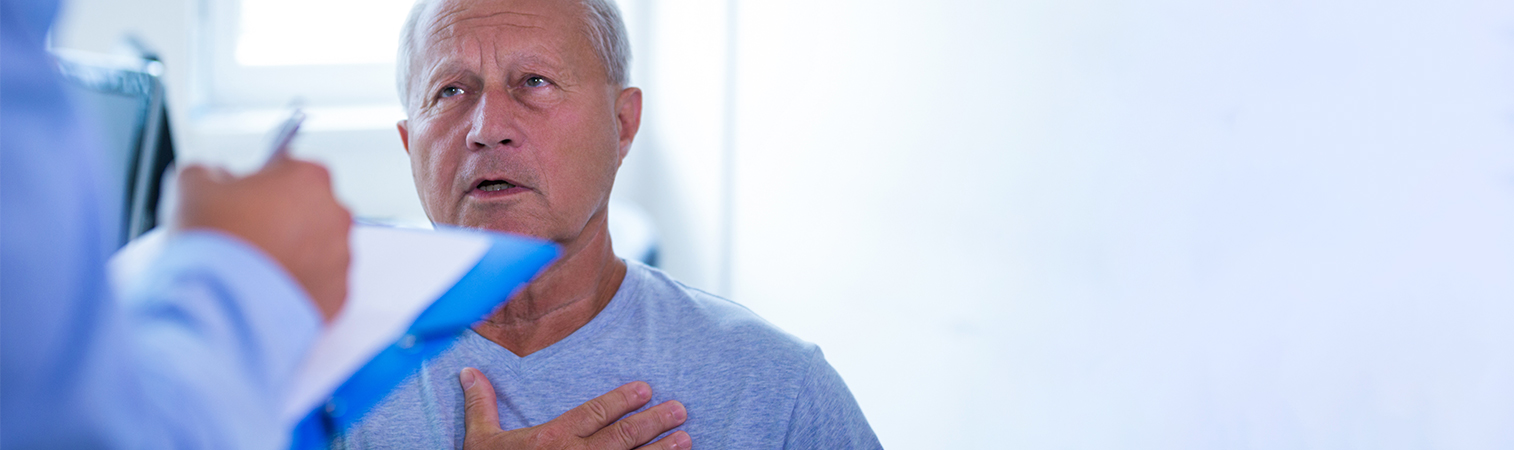
Cardiac tumors that are asymptomatic in the initial stages develop symptoms as they continue to spread. These symptoms are not of a single type but can be observed in many different types. Different symptoms occur depending on the location of the heart and the type of tumor. Suddenly, heart tumors begin to affect a person’s life badly. The symptoms of cardiac tumors are as follows:
- Swelling of the legs
- Fatigue
- Chest discomfort
- Difficulty breathing
- Weight loss
- Fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
- Sweating at night
- High fever
- Joint pain
- Blurred consciousness
- Difficulty speaking
Cardiac Tumors Risk Factors
There are some risk factors for cardiac tumors, the exact cause of which is unknown. Tumors are a health problem that usually occurs with advancing age. Therefore, being of advanced age is a risk factor for this disease. This disease is also linked to genetic factors and can be caused by a history of tumors in parents and close relatives. Mutations in the DNA chain are also a cause. In addition, the repair of these mutations decreases with age. Finally, a weakened immune system is also a risk factor for cardiac tumors.
Cardiac Tumors Complications
When cardiac tumors are malignant and progress, they can cause several health problems. Therefore, there are many complications associated with these tumors. Complications of cardiac tumors include:
Heart Failure: The growth of the tumor can obstruct blood flow. This can lead to impaired heart function and heart failure.
Pericardial Effusion: Tumors can cause fluid to build up around the heart, which can lead to pericardial effusion.
Embolism: When tumor fragments cause blockages in blood vessels, other organs can be damaged. This is called an embolism in medical language.
Valvular Dysfunction: Cardiac tumors can affect the heart valves, causing valvular dysfunction and insufficiency. This can lead to symptoms of shortness of breath and fatigue.
Arrhythmias: Cardiac tumors affect the normal electrical conduction of the heart. Some arrhythmias can therefore occur. The most common of these arrhythmias may be fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.